What are the Symptoms and Causes of Bladder Cancer?
What are the Symptoms and Causes of Bladder Cancer?
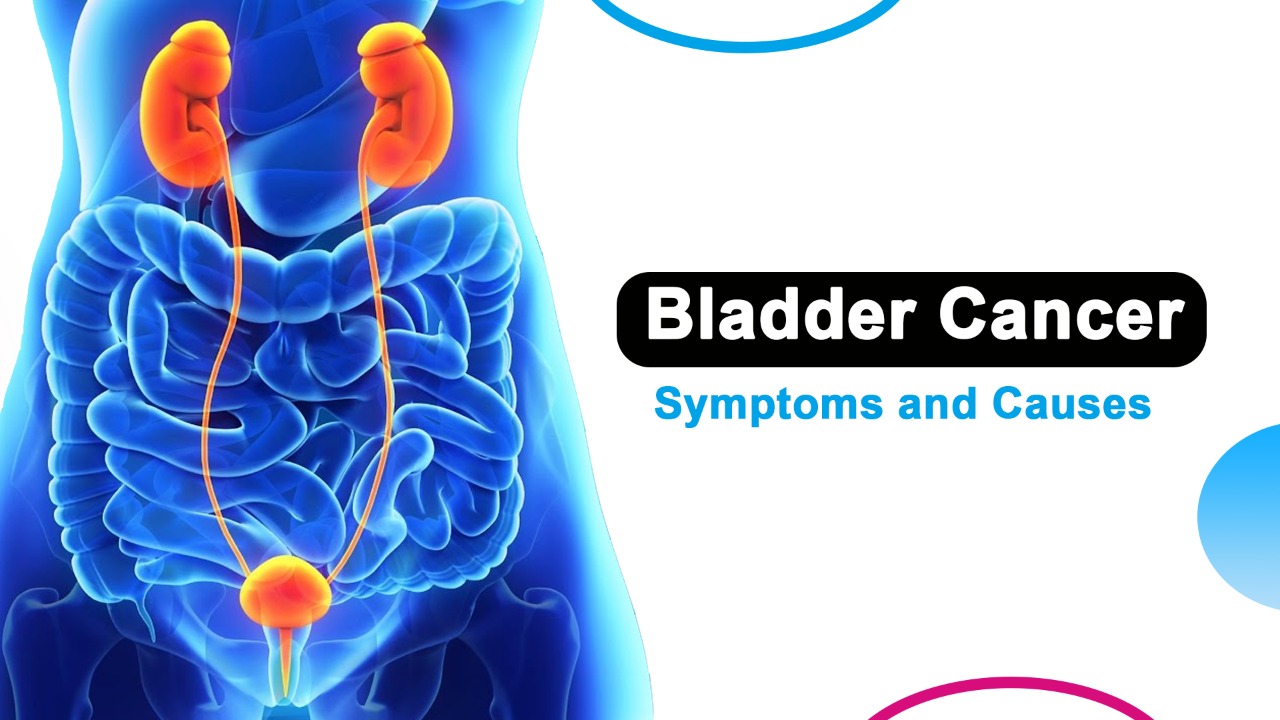
What is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that arises from the cells that line the bladder. These cells can become abnormal and start to grow, leading to the development of bladder cancer. If you notice any changes in your bladder or if it feels more painful than usual, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Bladder cancer is cancer that develops from the cells that line the bladder. It is the most common type of cancer in men. The average age at which bladder cancer is diagnosed is about 75 years old.
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that affects the bladder. It can be a very serious condition, and if not treated quickly, it can lead to death. There are many symptoms of urinary bladder cancer, and if you are concerned about your health, you should see a doctor about it.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
The classical symptom of bladder cancer is painless hematuria (blood in the urine). Other symptoms may include:
Increased frequency of urination
Urinary obstruction caused by clots or a growing tumor inside the bladder
Most Common Types of Bladder Cancer
The most common type is Transitional Cell Carcinoma (also called Urothelial Carcinoma). Less common types include:
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
How to detect bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is not among the most common cancers in men and women, so regular screening is generally not done unless symptoms appear.
The easiest and gold standard method to detect bladder cancer is an office-based cystoscopy, where a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the urethra to directly view the bladder lining.
If bladder cancer is suspected, your doctor may:
Perform a physical examination
Order tests such as urinalysis to detect blood or abnormal cells
Recommend a biopsy to confirm malignancy
Use ultrasound or CT scan to visualize tumors or abnormalities inside the bladder
If you notice painless blood in urine or experience unusual urinary symptoms, it’s important to consult your doctor promptly. Early detection improves treatment outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors of Bladder Cancer
There is no proven genetic inheritance linked to bladder cancer. Common causes and risk factors include:
Smoking – the most significant risk factor
Alcohol consumption
Exposure to industrial chemicals like vinyl chloride
Chronic bladder infections (especially from long-term Foley’s catheter use)
Parasitic infections like Schistosoma haematobium (linked to squamous cell carcinoma)
Other factors include:
Age – more common in older adults
Gender – men are more frequently affected than women
Occupational exposure – working in industries involving dyes, rubber, or leather
Treatment for Bladder Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer. Options may include:
Surgery – to remove tumors or even the entire bladder in advanced cases
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
Immunotherapy – in certain cases
Final Thoughts
Bladder cancer is a serious but treatable condition if detected early. If you experience painless blood in the urine or any persistent urinary symptoms, do not ignore them. Timely diagnosis through cystoscopy and other tests can help start the right treatment plan.
Always consult a medical professional for guidance and never hesitate to get checked if something feels off.
You May Also Like
Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery: A Minimally Invasive Breakthrough in Oncologic Care Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery: A Minimally …
Early signs of thyroid cancer- by Dr. Vijay Jagad Early signs of thyroid cancer- by …
Understanding Colon Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis Understanding Colon Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis Updated …