Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery: A Minimally Invasive Breakthrough in Oncologic Care
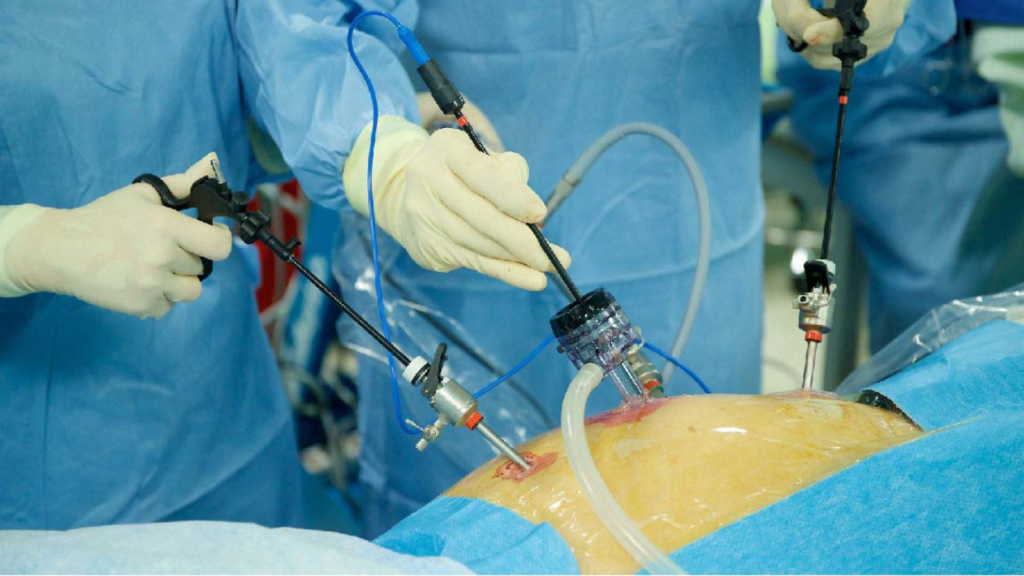
Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery: A Minimally Invasive Breakthrough in Oncologic Care Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery: A Minimally Invasive Breakthrough in Oncologic Care- by Dr. Vijay Jagad Updated On: 9. May 2025 Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery, also known as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery, is a method for the extirpation of cancer from the abdomen and thorax. This approach offers several advantages, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter recovery times, and smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. Similarly, laparoscopic cholecystectomy has become the gold standard for treating gallbladder-related diseases. Since its introduction in the late 1980s, it has largely replaced open cholecystectomy due to its minimally invasive nature, leading to quicker recovery and fewer complications. Furthermore, large-scale trials such as the COLOR II and COST studies have demonstrated that laparoscopic colorectal surgery is a standard approach for treating colon and rectal tumors. These trials have shown that laparoscopic techniques offer outcomes comparable to open surgery, with benefits like reduced blood loss and faster recovery times. Proven Effectiveness in Cancer Treatment One of the most well-known laparoscopic procedures is laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which has become the gold standard for treating gallbladder-related diseases. Encouraged by its success, many international clinical trials, including COLOR II and COST, have validated the use of laparoscopic colorectal surgery for colon and rectal cancers. Consequently, these studies have demonstrated that laparoscopic surgery is as safe and effective as open surgery, with added benefits for patient recovery. Advantages of laparoscopic surgery: 1. During laparoscopic surgery we also peritoneoscopy to look for operability, so this helps us for staging.2. laparoscopic surgery uses small 1 cm size incision so it is less painfull and patient needs less post operative painkillers.3. Recovery of patients after laparoscopic surgery is faster and discharge from from hospital is early.4. Cosmetically laparoscopic surgery is better than open surgery.5. Every cancer patient needs postoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy and tolerance to these toxic treatments is superior in patients who have undergone laparoscopic surgery.Laparoscopic approach has been used for almost all cancer of abdomen. Versatility Across Abdominal Cancers Today, the laparoscopic approach is used for a wide range of abdominal cancers, including but not limited to: Colorectal cancer Gastric (stomach) cancer Pancreatic cancer Liver cancer Adrenal tumors Its application continues to expand as surgeons gain more expertise and technology continues to evolve. Conclusion Laparoscopic cancer surgery represents a major step forward in the treatment of abdominal and thoracic malignancies. By combining safety, precision, and patient comfort, this minimally invasive technique is quickly becoming the preferred choice for cancer surgeries worldwide. With shorter hospital stays, reduced pain, quicker recovery, and better cosmetic results, laparoscopic surgery offers both clinical and quality-of-life benefits for patients fighting cancer. Leave a Reply Cancel Reply Logged in as Dr Vijay Jagdish Jagad. Edit your profile. Log out? Required fields are marked * Message* You May Also Like Early signs of thyroid cancer Early signs of thyroid cancer • April 8, 2025 • Blog Early signs of thyroid cancer- by Dr. Vijay Jagad Early signs of thyroid cancer- by … Understanding Colon Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis Understanding Colon Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis • April 8, 2025 • Blog Understanding Colon Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis Understanding Colon Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis Updated … What are the Symptoms and Causes of Bladder Cancer? What are the Symptoms and Causes of Bladder Cancer? • April 8, 2025 • Blog What are the Symptoms and Causes of Bladder Cancer? What are the Symptoms and Causes …